Balsam Fir
Abies balsamea
Overview
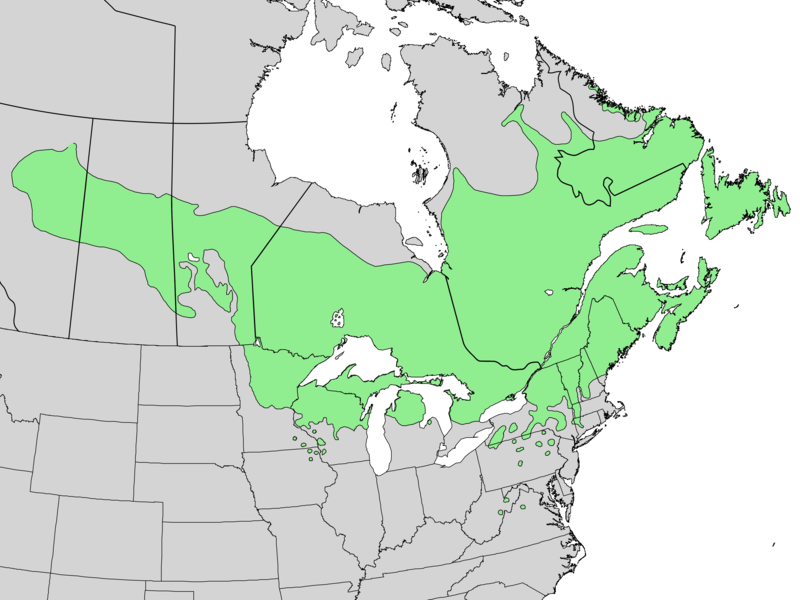
Native to cooler regions north of Belleville. Popular Christmas tree but challenging as landscape specimen in zone 5
Balsam fir is iconic tree of northern forests and source of Canada balsam resin
Full Tree
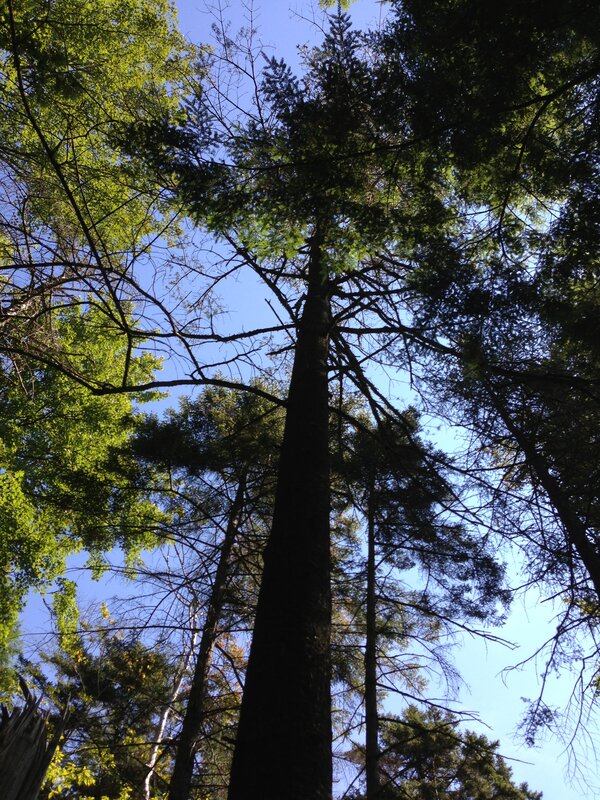
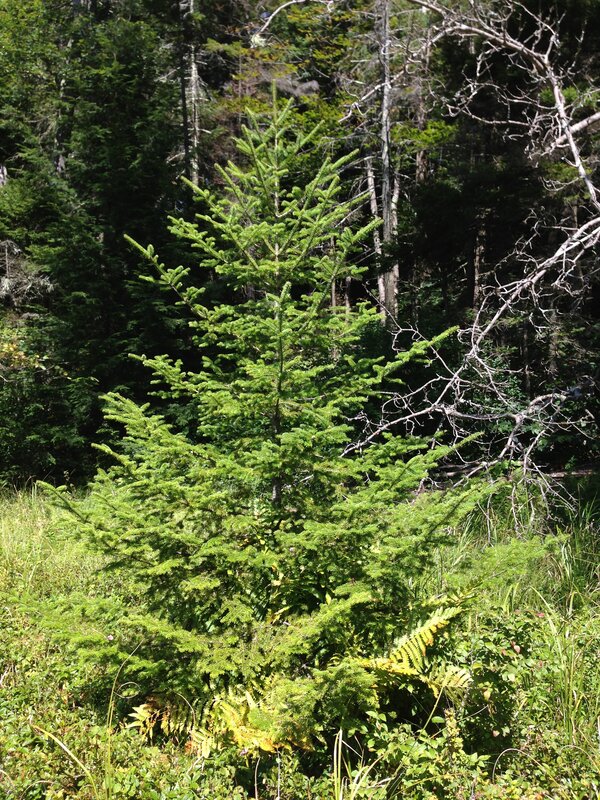


Identification
Leaves
Flat, dark green needles with two white stripes underneath. Needles are blunt-tipped (not sharp) and strongly aromatic when crushed.
Leaves

Bark
Young bark is smooth and gray with prominent resin blisters. Matures to scaly gray-brown bark.
Bark


Flowers
Male cones are yellowish, female cones are purple, appearing in spring.
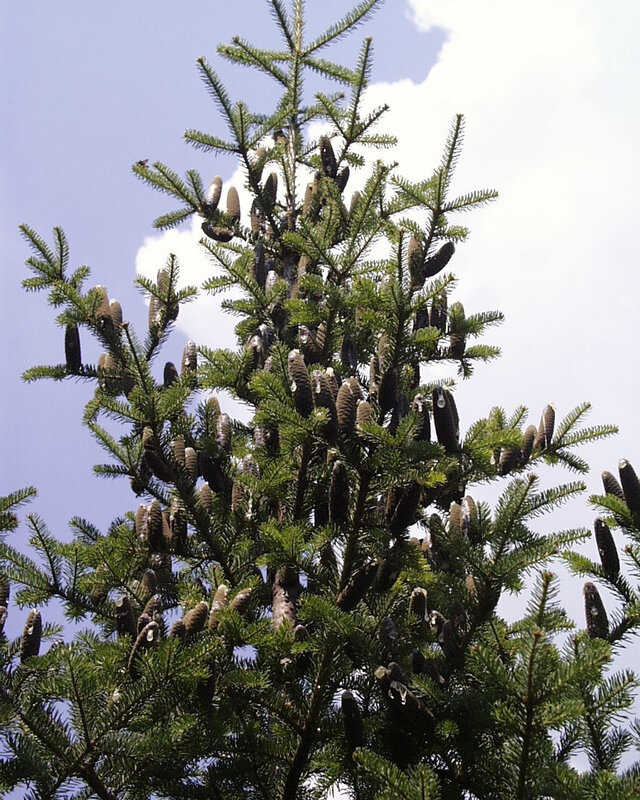
Fruit
Upright cylindrical cones (2-4 inches) sitting on top of branches. Cones disintegrate on tree when ripe, leaving central spike.
🦆 Valuable wildlife food source
Growing Conditions
Climate
Better suited to zones 2-4a. Struggles with heat in zone 5 Belleville
Hardiness Zones: 2, 3, 4a, 4b, 5a
Light Requirements
Soil
Moisture: moist
Drainage: well-drained, moderate
pH Range: 5 - 6.5
Tolerance
Care & Maintenance
Pruning
Best Season: February-April
Frequency: Minimal pruning needed
- Remove only dead or damaged branches
- Maintain natural form
- Avoid heavy pruning
Avoid: No specific restrictions
Watering
Establishment: Regular watering for first 2 years
Mature: Requires consistent moisture
Seasonal Care Timeline
Spring
- Check for spruce budworm activity
- Monitor health after winter
- Strong fragrance from new growth
Summer
- Heat stress in Belleville climate (zone 5)
- Requires adequate moisture
- Monitor for spruce budworm and needle cast
Fall
- Popular as Christmas tree
- Assess health
- Ensure adequate moisture before winter
Winter
- Snow load on dense branches
- Salt damage from roads
- Attractive winter evergreen
Common Issues
Spruce Budworm
ModerateDefoliating caterpillar that feeds on new growth
Symptoms: Browning needles, Defoliation of new growth, Webbing on branch tips
Treatment: Biological insecticides if severe, often not necessary
Prevention: Maintain tree health, monitor populations
Needle Cast Diseases
ModerateFungal diseases causing needle browning and drop
Symptoms: Browning needles, Premature needle drop, Thinning appearance
Treatment: Improve air circulation, fungicide if severe
Prevention: Ensure good drainage and air flow
Urban Stress
ModeratePoor adaptation to urban conditions
Symptoms: Needle browning, Thinning crown, Slow growth, Decline
Treatment: Improve growing conditions, ensure adequate moisture
Prevention: Plant in suitable locations only - cool, moist sites
Sources & References
Information compiled from the following authoritative sources:
Quick Facts
When to Call an Arborist
Recommended inspection: Annual inspection recommended
- •Significant needle loss
- •Extensive defoliation
- •Overall decline
- •Not thriving in location
- •Heat stress symptoms
Free consultation for Belleville residents
Recommended Services
Based on Balsam Fir characteristics
