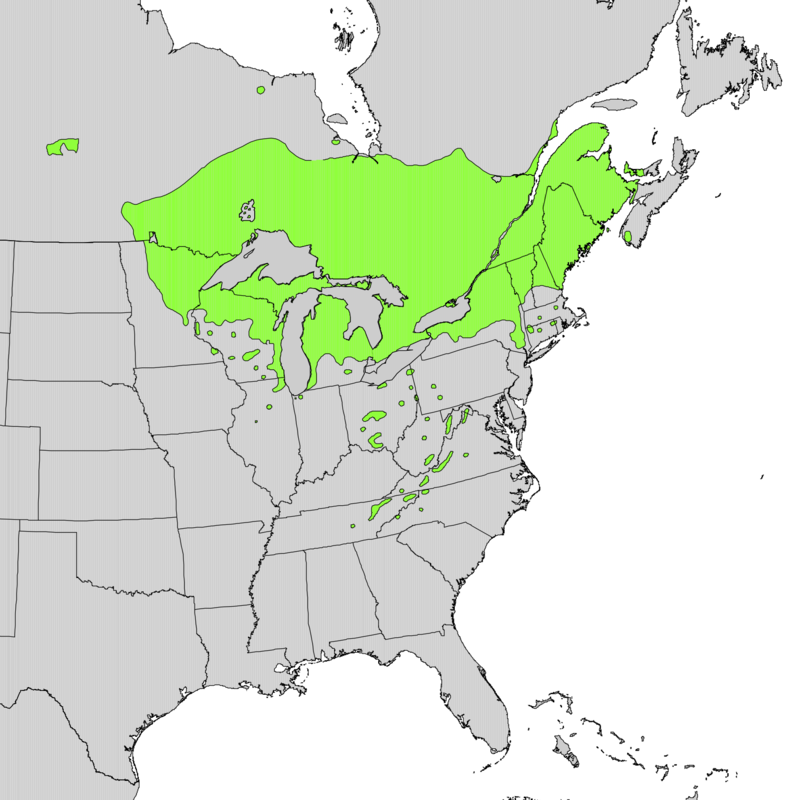
Eastern White Cedar
Thuja occidentalis
Overview
Important native evergreen for wildlife habitat, windbreaks, and privacy screens
Indigenous peoples used the wood and bark for various purposes including canoe frames and medicine
Full Tree
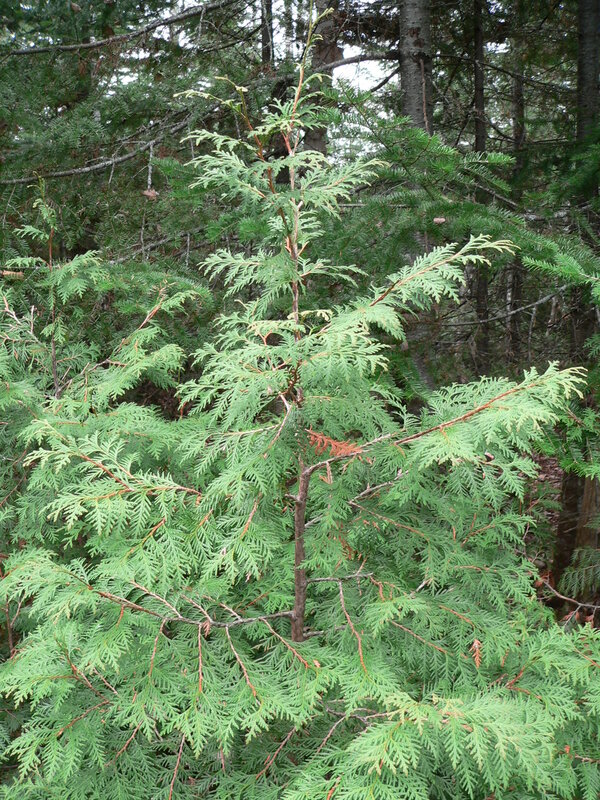
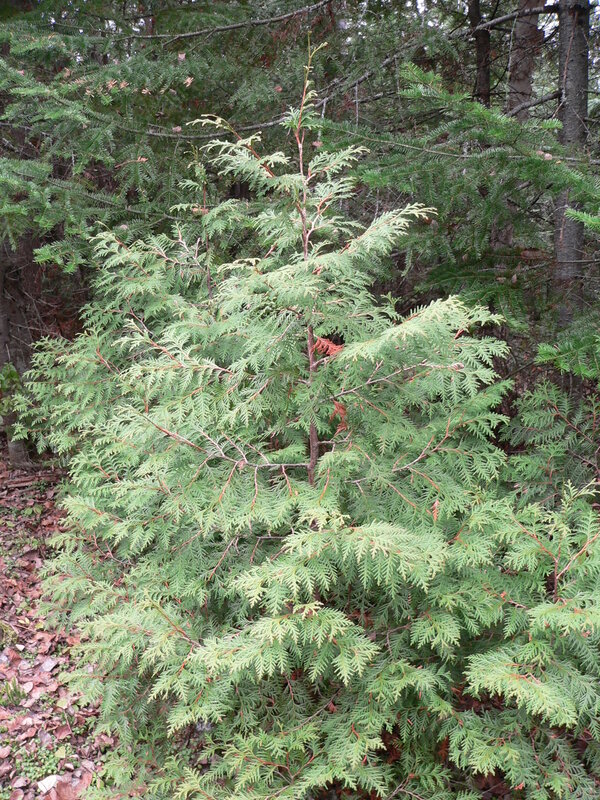


Identification
Leaves
Small scale-like leaves arranged in flattened sprays. Foliage often bronzes in winter, returning to green in spring.
Leaves

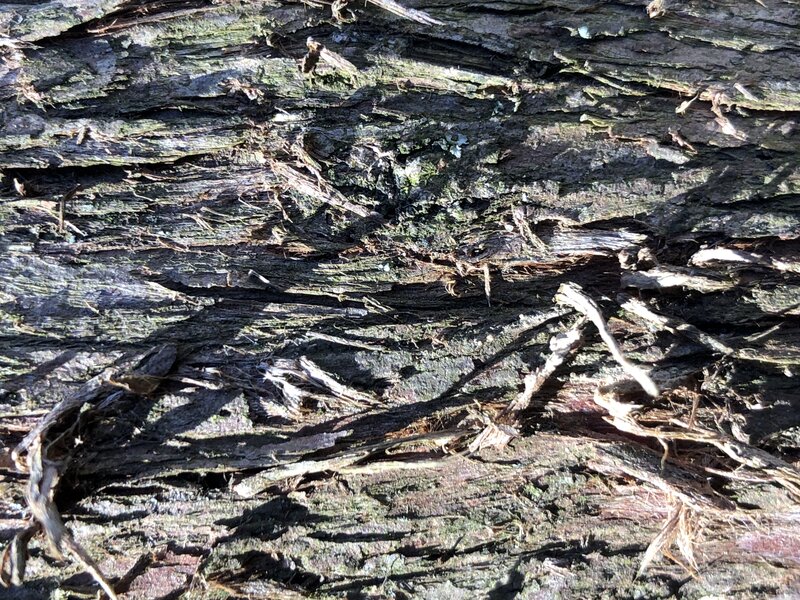
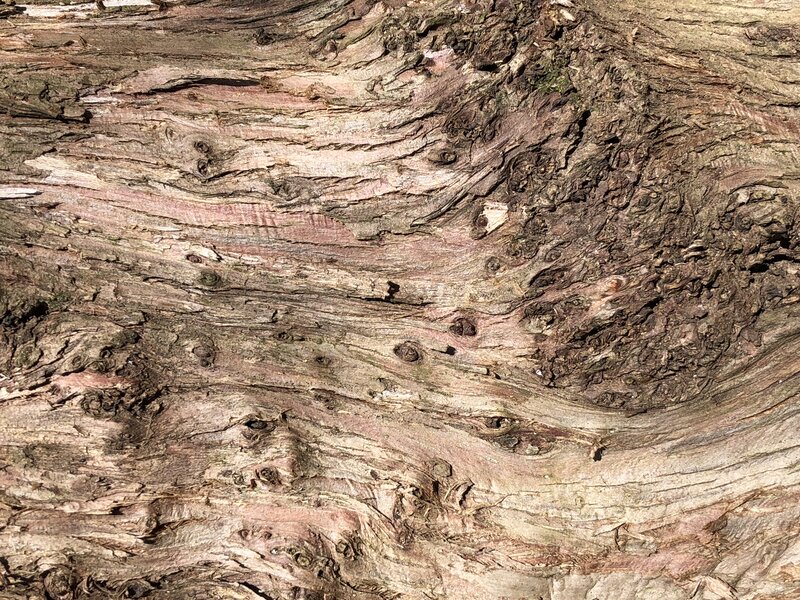
Bark
Thin fibrous bark that shreds vertically in narrow strips, gray-brown to reddish-brown in color.
Bark


Flowers
Inconspicuous male and female cones appear in spring on same tree.
Fruit
Small upright cones (1 cm) with 8-12 overlapping scales, maturing in fall.
🦆 Valuable wildlife food source
Growing Conditions
Climate
Excellent cold hardiness and adapted to wet sites common in Eastern Ontario
Hardiness Zones: 2, 3, 4a, 4b, 5a, 5b
Light Requirements
Soil
Moisture: moist, wet
Drainage: moderate, poor
pH Range: 6 - 8
Tolerance
Care & Maintenance
Pruning
Best Season: May-July
Frequency: Annual light pruning for hedges, minimal for specimens
- Prune in May-July after new growth hardens
- Do not cut into old wood - will not regrow
- Shape hedges annually for density
Avoid: October-November to prevent winter damage to cut areas
Watering
Establishment: Regular watering for first 2 years
Mature: Prefers consistent moisture
Seasonal Care Timeline
Spring
- Check for winter damage and prune
- Bronze foliage should green up
- Monitor for leafminer activity
Summer
- Watch for drought stress
- Monitor for cedar leafminer and bark beetle
- Good time for hedging
Fall
- Foliage may begin to bronze
- Water thoroughly before ground freezes
- Assess overall health
Winter
- Heavy snow can cause branch breakage
- Shield from road salt spray
- Foliage bronzing is normal
Common Issues
Cedar Leafminer
LowSmall moth larvae that mine cedar foliage
Symptoms: Brown needle tips, Yellowing foliage, Needle drop
Treatment: Systemic insecticide if severe, often not necessary
Prevention: Maintain tree vigor, adequate moisture
Winter Browning
ModerateFoliage damage from winter desiccation and salt
Symptoms: Brown foliage, Needle drop, Branch dieback
Treatment: Prune damaged branches in spring, ensure adequate fall watering
Prevention: Anti-desiccant spray, burlap screens, avoid salt exposure
Sources & References
Information compiled from the following authoritative sources:
Quick Facts
When to Call an Arborist
Recommended inspection: Annual inspection recommended
- •Extensive browning or dieback
- •Significant pest infestation
- •Structural damage from snow/ice
- •Root damage or decay
- •Disease symptoms
Free consultation for Belleville residents
Recommended Services
Based on Eastern White Cedar characteristics
